Dental Blog - HANNIBAL, MO
Tips, Facts, And The
Latest In Dentistry

The Dental Implant Screw: What To Know About Robotic Placement
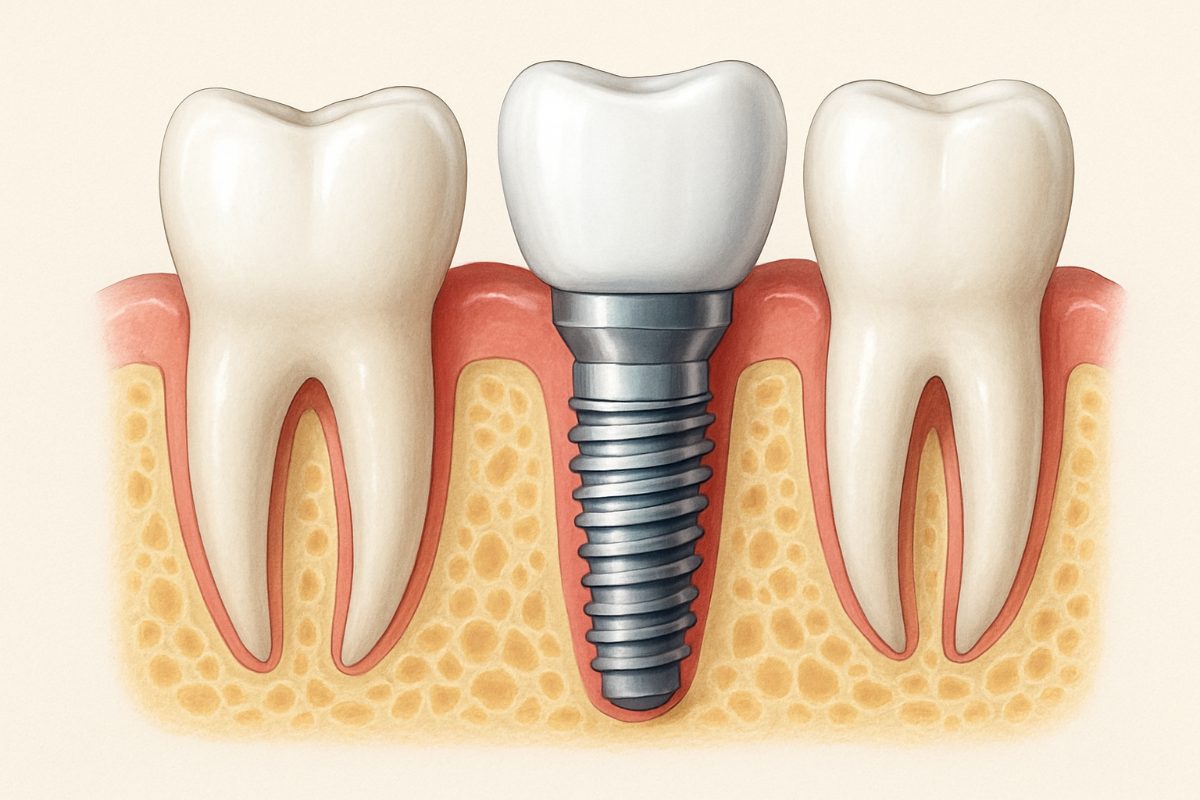
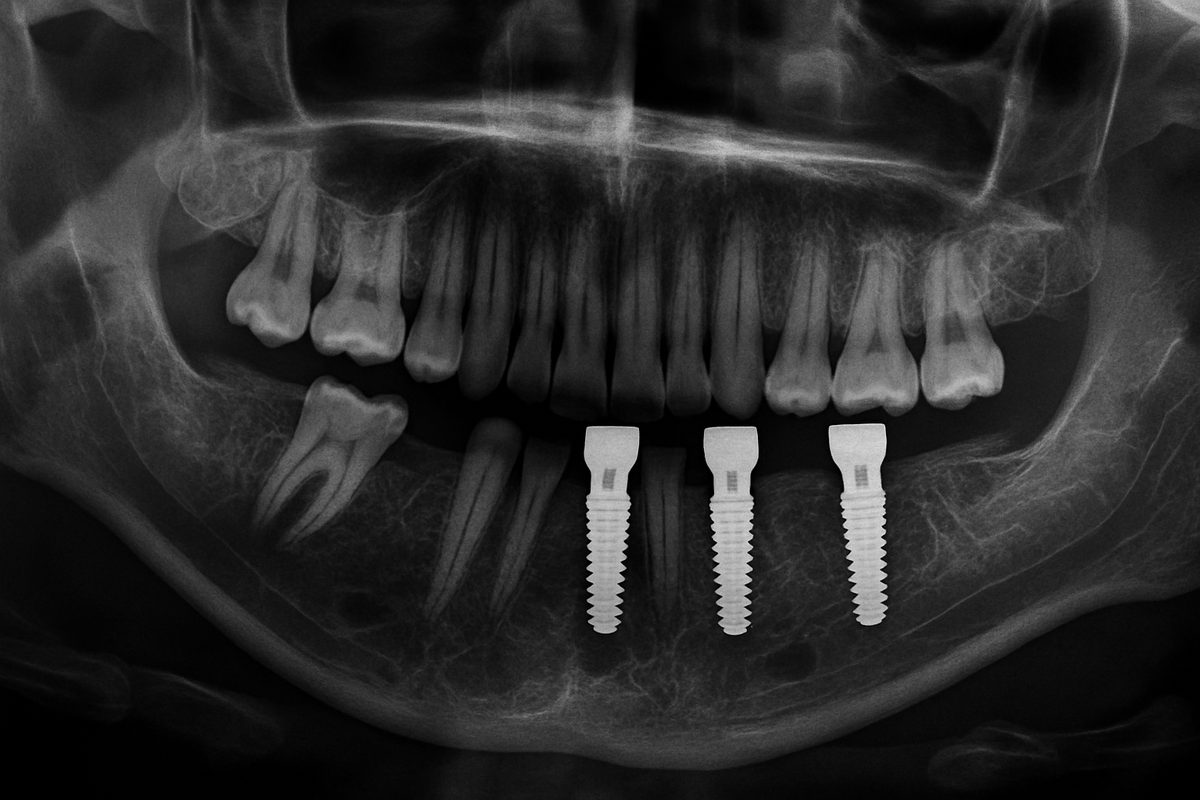
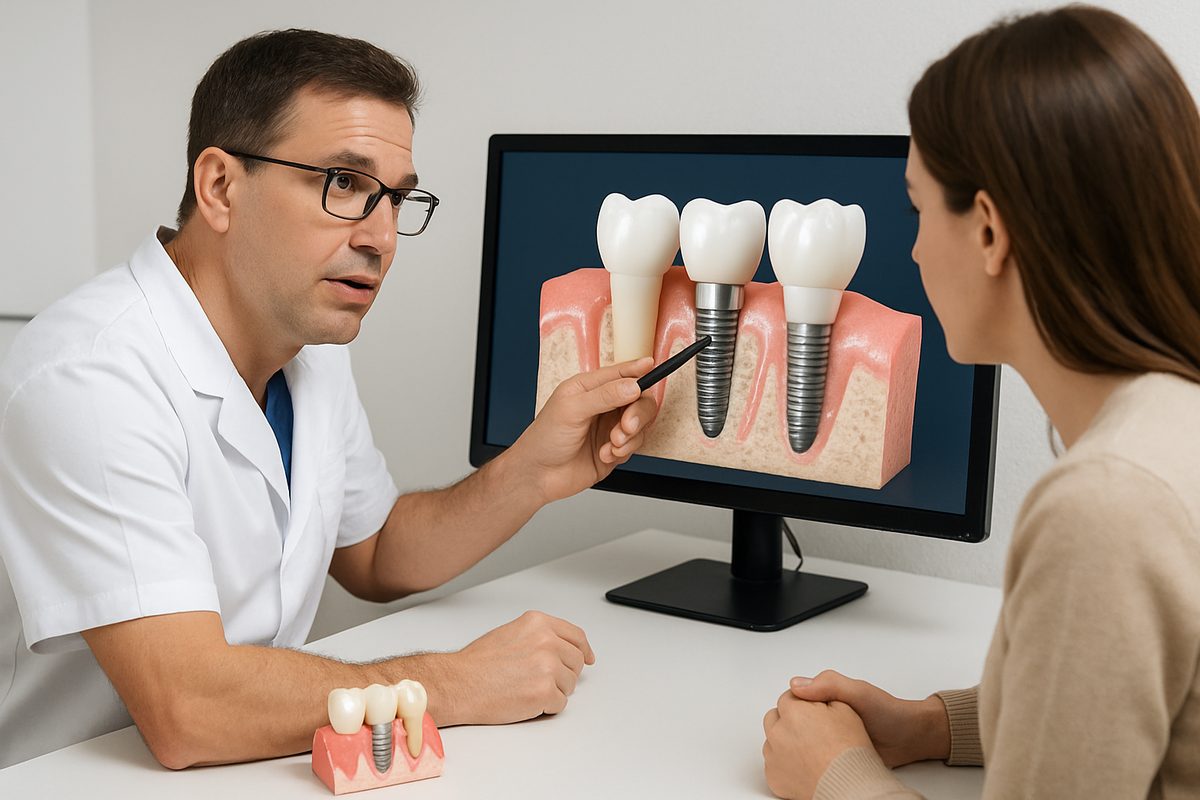
A screw dental implant is a common way to replace a missing tooth. It uses a threaded metal fixture that is placed into the jawbone, then fitted with an abutment and crown. New technology like the YOMI robot is changing how dentists place screw dental implants by combining 3D planning with guided, haptic-assisted drilling to improve accuracy and predictability.
What Is a Screw Dental Implant?
A screw dental implant is an implant shaped like a screw that acts as an artificial tooth root. The main parts are the fixture (the screw that goes into bone), the abutment (connects screw to crown), and the crown (the visible tooth). The screw design helps anchor the implant and promotes osseointegration — the bone bonding to the implant for long-term stability.
Types and Materials of Implant Screws
Materials
Implant screws are most often made from titanium or titanium alloys because they are strong and well tolerated by bone. Zirconia implants offer a metal-free option with good biocompatibility for some patients. Material choice affects strength, aesthetics, and how the body responds during healing.
Designs and Sizes
Screws come in many thread patterns, diameters, and lengths. Narrow screws suit front teeth or thin bone; wider, longer screws give more support in molar areas. Thread design influences how forces spread to bone and how quickly the implant integrates, so clinicians match the screw to bone quality and tooth location.
How Robotic Placement Works: The YOMI Robot
YOMI uses a 3D CT scan to plan the exact position, angle, and depth of the screw dental implant. During surgery the dentist follows YOMI’s haptic guidance: the robot allows the planned motion while resisting deviations. The clinician remains in control, performing drilling and placement with real-time navigation and tactile feedback for precise execution.
Benefits of YOMI Robotic Placement for the Screw Dental Implant
Robotic assistance improves placement accuracy and angulation, which helps the screw sit where bone support is best. This reduces the risk of injuring nerves or sinuses and can improve the long-term fit of the abutment and crown. More predictable placement also lowers the chance of needing corrective surgery later.
What to Expect During a Robotic Screw Dental Implant Procedure
You’ll have a 3D scan and a treatment plan first. On the day, local anesthesia is given, and the dentist uses YOMI to guide pilot drilling, then places the implant screw to the planned depth. Procedures are often similar in time to conventional implant placement. Recovery includes usual swelling and short-term discomfort.
Risks, Limitations, and When Robotic Assistance May Not Be Ideal
Risks still include infection, delayed healing, or screw loosening. In complex cases needing open surgery or extensive bone grafting, robotic guidance may be less useful, and freehand techniques or staged approaches could be better. Clinician judgment remains key even with robotic tools.
Aftercare and Longevity of a Screw Dental Implant Placed with YOMI
Aftercare includes good oral hygiene, a soft diet for a few days, and follow-up visits to check healing. Watch for persistent pain, swelling, or loosening. Precise placement from YOMI supports proper load distribution, which helps implants last many years when maintained.
How to Choose a Provider Who Uses Robotic Placement
Ask about the dentist’s experience with the YOMI robot, request case examples, and review pre-op and post-op imaging. Look for training in implant dentistry and surgical experience. Remember robotics assist but do not replace a skilled surgeon’s decision-making.
Brief Practice Note and Call to Action
Our practice uses the YOMI robot to plan and place screw dental implants with careful imaging review. Schedule a consult and CT scan to see if robotic-assisted implant treatment is right for you.